Last Updated on: October 16, 2024
Table of Content
Statistics show that 5 million people across the world develop OHCA (Out-of-the Hospital Cardiac Arrest) each year, and only 7% of them survive. As a crucial part of the chain of survival, airway management has always been a major focus of research in recent years.
If you are a paramedic, you instinctively know that the most critical task you will perform is managing the airway. Whether your victim is struggling to breathe through infected lungs or drawing in their clogged-clogged airways, administering proper airway management techniques becomes paramount to save a life.
Learning effective techniques will ensure successful outcomes during BLS (Basic Life Support). It will enhance the oxygen delivery to the lungs and circulation to vital organs, significantly improving the chances of recovery and survival.
In this blog, we will explore the airway management techniques in BLS, strategies and best practices for various scenarios. Let’s get started!
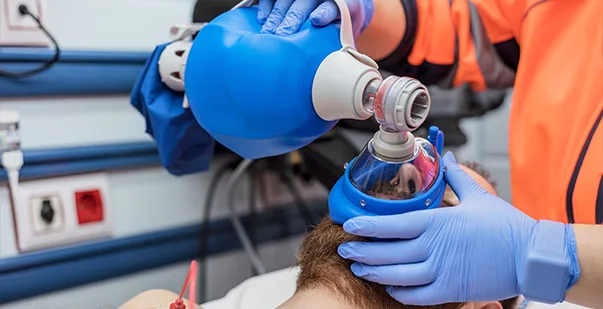
Basic Life Support (BLS) refers to a set of essential medical techniques and interventions that provide immediate care to victims experiencing life-threatening emergencies. The technique is usually administered by healthcare professionals, first responders, or tainted vilniaus. The primary focus of BLS is to support and sustain the vital functions of the victim.
Establishing and maintaining a clear and unobstructed airway is one such goal of BLS. It aims to stabilize the victim’s condition and improve the chance of survival until advanced medical care arrives. Here are the key objectives of airway management in BLS.
Read More: BLS Meaning: What Does BLS Stand For and Why It’s Important?
Now that you know the significance of airway management in BLS, you might be wondering what steps you should follow to open the airway. During airway management, several techniques can be used to open the airway and ensure optimal ventilation and oxygenation. The choice of the technique depends on the victim’s condition and the provider’s skill level. Here are some common techniques.
The Head-tilt-chin-lift technique is a basic maneuver used to open the way by aligning the oral and pharyngeal structures. This method of non-invasive airway management is commonly administered when there is no suspicion of neck or spinal injury. The procedure is easy to perform to establish a patient away and enable effective ventilation.
Here’s how to open the airway for breaths using the Head-tilt-chin-lift technique.
Jaw Thrust Maneuver is one of the alternative open airway techniques used when there is a possibility of neck or spinal injury in the victim. This airway management technique avoids movement or any manipulation of the victim’s head and neck. It is particularly applicable in circumstances where the stability of the victims’ cervical spine is damaged. It minimizes the risk of exacerbating the existing neck of spinal injury while enabling effective airway management.
However, how do you open the airway using the jaw thrust maneuver technique? The steps are below.
If you need to open a patient’s mouth to suction the oropharynx, you need to perform a finger swipe or insert an oral airway. This technique to open the airway is the most commonly used and is known as the cross-finger method. To perform the procedure, it is always required to follow the standard precautions. The steps in cross finger technique include the following:
Read More: Why is BLS Certification Required for an Emergency Medical Team Member?
Managing a patient’s airway plays a crucial role in emergency medicine and healthcare. It involves keeping their airway open to ensure adequate air gets to the lungs. Learning the proper airway management techniques through comprehensive certification training will provide you with a way to establish and maintain your credibility. By integrating proper techniques into BLS protocols, you can improve your ability in maintaining the airway’s patency in the chain of survival.
Airway management is an evolving and dynamic field, with continuous research and advancements contributing to improved patient outcomes. Therefore, it is important to stay updated on the latest guidelines and techniques to deliver the best care for the victims.