Table Of Content(s)
- BLS Meaning: What does BLS stand for?
- What are the key components and techniques involved in Basic Life Support?
- What are the emergencies that need Basic Life Support interventions?
- Conclusion
If you are working in emergency medical care, you need to understand the terms associated with basic life support or BLS. By enrolling in a BLS class you can master lifesaving skills to sustain life in emergencies. Helping over 50,000 people annually, basic life support is a crucial part of emergency medical care. A comprehensive BLS course covers cardiopulmonary resuscitation techniques, airway management along with innovative techniques to relieve airway obstruction. Whether you are a healthcare professional, a potential first responder or simply a concerned citizen, learning the skills of Basic Life Support can mean the difference between life and death. In this blog, we will explore the key components and techniques involved in basic life support.
What are the key components and techniques involved in Basic Life Support?
Basic Life Support teaches skill set that forms the backbone of emergency medical response. It involves key components and techniques that support life in various emergencies. These elements ensure that first responders can provide immediate care effectively without having to wait for advanced medical help to arrive.
Key components and techniques involved in Basic Life Support:
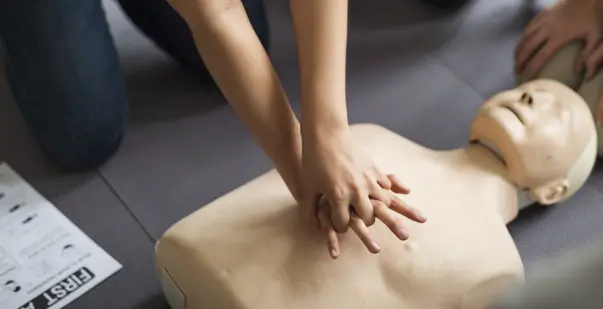
Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation (CPR):
- Chest Compressions: Delivering high-quality chest compressions at a rate of 100-120 compressions per minute to maintain blood circulation.
- Rescue Breaths: Providing ventilations to ensure oxygen reaches the lungs and bloodstream.
- Compression-to-Ventilation Ratio: For adults, a ratio of 30:2 is used, meaning 30 compressions followed by 2 breaths.
Automated External Defibrillator (AED) Use:
- Defibrillation: Using an AED to deliver an electric shock to the heart to restore a normal rhythm in cases of sudden cardiac arrest.
- Pad Placement: Correctly placing the AED pads on the patient’s chest as indicated on the device.
Airway Management:
- Head-Tilt/Chin-Lift Maneuver: To open the airway in an unconscious patient.
- Jaw-Thrust Maneuver: Used especially in cases of suspected spinal injury to open the airway without moving the neck.
Relieving Airway Obstructions:
- Heimlich Maneuver (Abdominal Thrusts): For conscious adults and children to expel an object obstructing the airway.
- Back Blows and Chest Thrusts: For infants to relieve airway obstructions.
Rescue Breathing:
- Mouth-to-Mouth Ventilation: Providing breaths to a patient who is not breathing but has a pulse.
- Bag-Valve-Mask Ventilation: Using a bag-valve-mask (BVM) device to deliver breaths to a patient.
Team Dynamics:
- Effective Communication: Coordinating actions and communicating clearly with other responders to ensure a smooth and efficient rescue effort.
- Role Assignment: Assigning specific roles such as compressor, ventilator, and AED operator to optimize response efficiency.
Read More: What are the different levels of CPR certification training?
What are the emergencies that need Basic Life Support interventions?
Basic Life Support stands critical for several emergencies. These interventions are specifically designed to keep the victim stable till professional help arrives. Here are few common emergencies that need basic life support interventions:
- Cardiac Arrest: Sudden stopping of heart’s function, requiring immediate CPR and AED use to restore heart rhythm.
- Respiratory Arrest: When breathing stops, deliver rescue breaths and airway management to maintain oxygen supply.
- Choking: Airway obstruction by a foreign object, needing techniques like the Heimlich maneuver or back blows to clear the airway.
- Drowning: Victims of near-drowning incidents requiring rescue breaths and CPR to restore breathing and circulation.
- Severe Allergic Reactions (Anaphylaxis): Life-threatening allergic reactions causing airway swelling, treated with BLS techniques and epinephrine administration.
- Trauma and Severe Bleeding: Injuries causing significant blood loss, requiring pressure application, wound management, and CPR if the patient is unresponsive.
- Electrocution: Electrical injuries potentially leading to cardiac arrest, requiring immediate CPR and AED use.
- Drug Overdose: Overdoses causing respiratory or cardiac arrest, necessitating BLS interventions to support breathing and circulation.
- Unresponsive Patients: Any situation where a patient is unresponsive, needing assessment and potential CPR if they are not breathing or have no pulse.
Read More: The Ultimate Guide to CPR Certification for Non-Medical Professionals
Conclusion
BLS meaning, basic life support includes sets of fundamental skills that helps stabilize a patient in a critical medical emergency. Understanding what BLS stands for and the key interventions empower individuals to act swiftly and effectively during emergencies. Thus basic life support is not about just performing specific procedures. It is about preparing oneself to be responsible enough to save someone from a crisis.